Yasuhide Fumoto
Plucking CO2 from the Air Could Decarbonize Food, Fuel, and Fashion
Products made from carbon dioxide (CO2) captured from the atmosphere are part of a fast-growing trend to decarbonize nearly everything we use. Food, drink, fuel, and plastics can all be made using CO2 from the air. And recycling carbon could create a circular economy that vastly reduces pollution and waste.
Industrial activity over the past 250 years has greatly increased CO2 levels in our atmosphere and forced global warming. But companies like Twelve are turning this greenhouse gas into carbon-based products using water and solar energy. The firm aims to make sustainable automobile parts, jet fuel, washing detergent, and sunglasses using its photosynthesis technology.
Twelve’s electrolyzer technology turns CO2 and water into hydrogen, oxygen, and carbon monoxide to make base chemicals found in a wide range of commercial products. At industrial scale, the company estimates that its devices can remove as much CO2 as 120 billion trees.
Capturing and transforming CO2 in this way removes refined oil and gas from manufacturing. Companies free of reliance on fossil fuels are experimenting with carbon capture to reboot life-critical substances like food. Finnish company Solar Foods is using electrolyzed CO2 to grow its Solein protein, which replaces traditional agriculture plus its energy and greenhouse gas emissions.
Air Protein, a subsidiary of Kiverdi, uses the tagline ‘Meat Made From Air’ for its meat substitute products made from captured CO2. The company is using a technology pioneered by NASA to feed astronauts on long space journeys, where exhaled CO2 is used to feed microbes that are then turned into food.
Kiverdi has more than 50 patents pending and is exploring CO2 products to inject nutrients back into soil, feed farmed fish, and create biodegradable plastic.
Reducing plastic pollution is a global priority and a treaty signed by 173 countries aims to tackle the problem urgently. Captured CO2 is being targeted as a building block for a wave of replacement plastics, including biodegradable plastics made using sugar and wood waste.
Swiss activewear company On created its CleanCloud range of running shoes using plastic foam based on CO2 captured from industrial emissions. And Californian company Newlight has created the biodegradable CO2-derived AirCarbon for use in furniture, phone cases, packaging, sunglasses, and faux leather.
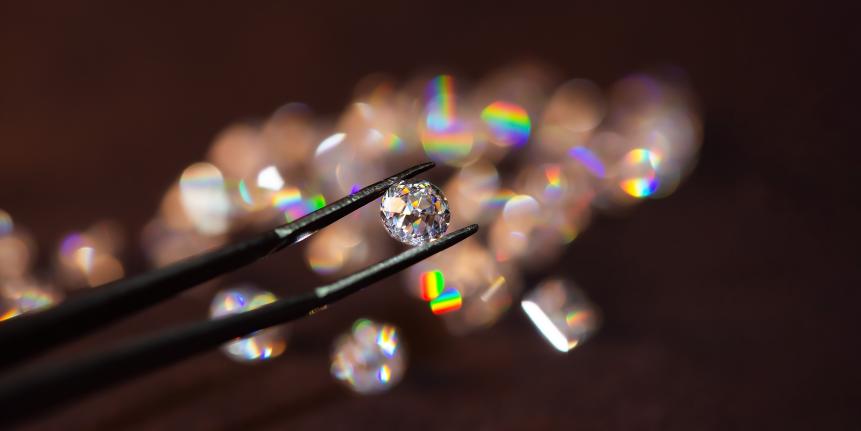
Luxury products are using similar carbon transformation technology. Vodka, perfumes, and even diamonds can all be crafted using atmospheric CO2, promoting positive climate impacts for expensive lifestyle items.

VichienPetchmai
Carbon dioxide can be used to create diamonds.
Advancing the concept of CO2 circularity in manufacturing will be vital to reaching net zero. Industries need to become carbon neutral, and then carbon negative, so their activity removes greenhouse gases from the atmosphere. Initiatives like New York Urban Future Lab’s ‘Carbon to Value’ initiative and the University of Michigan’s ‘Global CO2 Initiative’ are finding and promoting the companies and commercial processes to make that happen.
So far in 2022, the wheel has not turned far enough. The Circularity Gap Report shows that the world economy is less than nine percent circular, consuming way more virgin materials than it recycles and reuses. In 2019 global consumption of natural resources surpassed 100 billion metric tons.