Coneyl Jay
Emotional Robots: Machines that Recognize Human Feelings
Bridging the gap between simple automation and robots that can empathize and interact with humans naturally is a big challenge, but major progress has been made in the past few years.
Research into social robots has shown that machines that respond to emotion can help the most vulnerable, the elderly and children, and could lead to robots becoming more widely socially acceptable.
Robots that help care for others are often at the cutting edge of emotional interaction. Milo is both a robotic teacher and a student. Developers RoboKind created Milo to help children with autism spectrum disorders learn more about emotional expression and empathy while collecting data on their progress to target learning and treatment. Milo's friendly face makes him approachable and the children are able to analyze his expressions without feeling social anxiety.

wonry
White Coat Syndrome Fighters
Another situation where robots can reduce stress is in hospital settings. Expper Tech's 'Robin' was designed as a companion robot to provide emotional support for children undergoing medical treatment. Robin explains medical procedures to them, plays games and tells stories, and during treatment distracts them to reduce their perception of pain.
Expper's robot uses AI to create empathy, remembering facial expressions and conversations to build dialogue for follow-up sessions. In trials at the Wigmore Medical (UK) Pediatric Clinic in Yerevan, Armenia, the team found that Robin led to a 34% decrease in stress and an increase in happiness of 26% in the 120 children who interacted with him at least once.
Healthcare robots could all benefit from displaying emotional intelligence, both recognizing and responding to human emotions, and to some extent, managing them. The problem with this level of sophistication is the fear that human jobs may be lost as robots become more adept at handling social situations.
Population trends suggest that the demand for robots to work alongside people in care situations will grow over time. By 2050, the number of people aged 65 and over globally will be 1.6 billion (17%), roughly twice the proportion of what it is today. An extra 3.5 million care workers will be needed and that will include emotionally intelligent robots.
Today's simple systems are being trained to meet that demand. This includes ProxEmo, a little wheeled robot that can guess how you are feeling from the way you walk, and ENRICHME – the 'ambient assisted living' robot from the University of Lincoln in the UK – who helps older people to stay physically and mentally active.
miriam-doerr
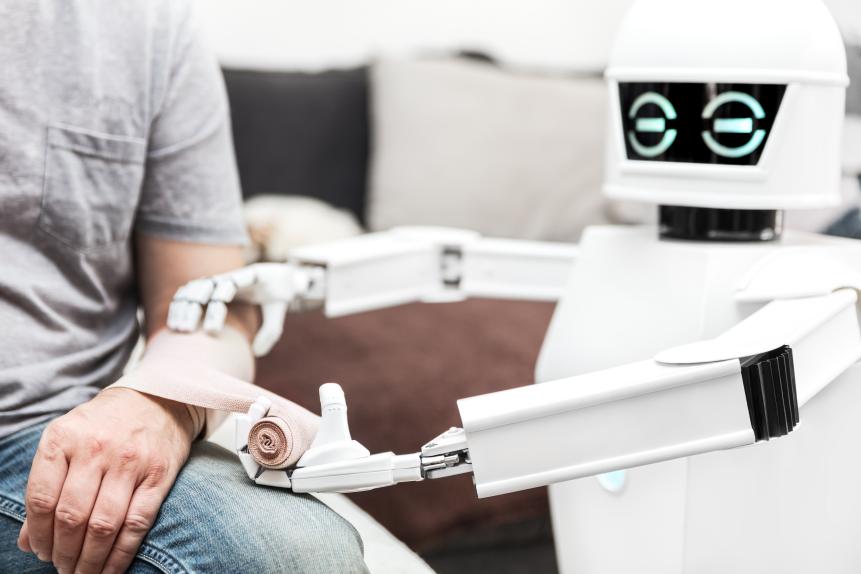
Assistance medicine service robot is putting a bandage on a arm of an male patient, at home in the bedroom.
A Rainbow of Emotions
Full-spectrum emotion AI will be needed to cope with the complexity of true human interaction, and that is the goal of organizations such as Affectiva. So far the company has trained its algorithms on more than nine million faces from countries around the world, to detect seven emotions: anger, contempt, disgust, fear, surprise, sadness, and joy.
Co-founder Rana el Kaliouby defined the category of 'emotion AI' and believes it will make robots smarter. She thinks devices will contain emotion chips as standard to respond to our needs in a more understanding way. Those technology companies could potentially use these advances to manipulate our emotions is a small risk compared to the benefits, she says.
The impact of social robots on our lives to date has been tiny. Manufacturers come and go without robots becoming a fixture in people's homes. But new and sophisticated models are being introduced that could make the breakthrough. Human emotions are difficult to define, but as trust in robots increases, cracking the psychological barrier becomes easier to imagine.