MARK GARLICK/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY
Take a Trip Through the Oort Cloud, It’s Fun

The most distant spacecraft launched by humans, Voyager 1, is currently 155 times farther away from the Sun than the Earth is. That’s almost four times more distant than Pluto, and the Voyager 1 craft has been traveling at over 38,000 mph for over four decades.
Indeed, Voyager 1 is so far away that it’s technically in interstellar space – it’s beyond the boundary where the charged particles that constantly rain from the Sun mix and mingle with the interstellar medium.
We’re not even getting started.
Beyond the planets, beyond the icy members of the Kuiper belt, beyond our more far-flung space probes, lies the very last remnant of the solar system: the Oort cloud. The Oort cloud contains billions of tiny fragments, each a mixture of ice and rock. These fragments, each no bigger than a few hundred meters across, are so far away from us that we’ve never directly observed any of them.
Instead, we can only guess as to the existence of the Oort cloud. The Dutch astronomer Jan Oort first made the conclusion in 1950 after studying the origins of long-period comets. These comets come from seemingly anywhere, and appear only once, making a single trip around the Sun before racing back off into the dark. He suspected that these comets had a home, a reservoir surrounding the solar system – the Oort cloud.
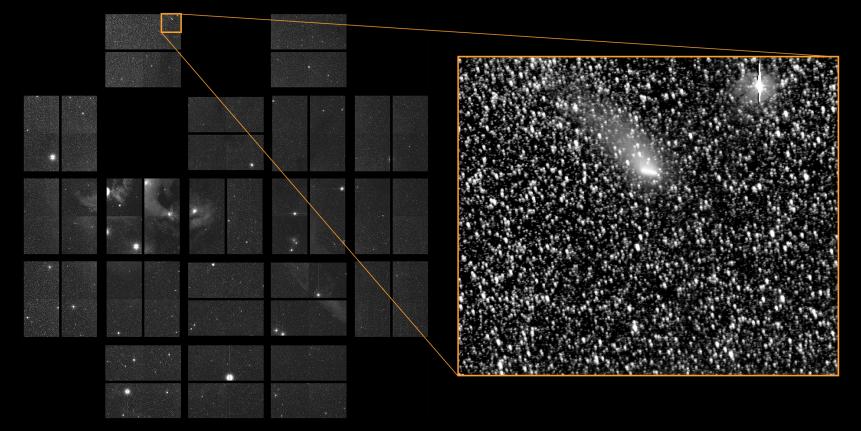

NASA Ames/W Stenzel; SETI Institute/D Caldwell
On Oct. 20, the Kepler spacecraft joined the fleet of NASA science assets that observed distant Oort Cloud native Comet Siding Spring as it passed through K2's Campaign 2 field-of-view on its long journey around the sun. The data collected by K2 will add to the study of the comet, giving scientists an invaluable opportunity to learn more about the materials, including water and carbon compounds, that existed during the formation of the solar system 4.6 billion years ago.
Astronomers believe that the inner edge of the Oort cloud sits about 1,000 AU (astronomical units, the distance between the Sun and the Earth) away. That means that Voyager 1 won’t reach it for another two centuries. Once it gets there, there won’t be any flashing lights or welcome banners. Despite hosting billions of individual comets, the volumes here are so tremendous that Voyager 1 will pass within ten million kilometers of one…if it’s lucky.
And the outer edge? Astronomers aren’t exactly sure where the Oort cloud cuts off, but it’s probably close to one or two light-years away, up to half the distance to our nearest neighbor star, Proxima Centauri. That means it will take Voyager tens of thousands of years before it finally passes through.
The Oort cloud represents the last true remnants of the formation of the solar system. When our system formed, it contained trillions of tiny bits of rock and ice that never got to form a planet. But as the planets formed, they stirred up the debris and flung them into the outermost edges of the solar system.
Even though the members of the Oort cloud live in interstellar space, they are still gravitationally connected to the Sun. But only weakly – even the tiniest of nudges can send them either scattering loose into the depths of space or plunging down into the inner solar system, where we recognize them as a comet.
It’s lonely out there.
Dive Deeper into the Universe
Journey Through the Cosmos in an All-New Season of How the Universe Works
The new season premieres on Science Channel and streams on discovery+.



















