Getty Images/John B. Mueller Photography
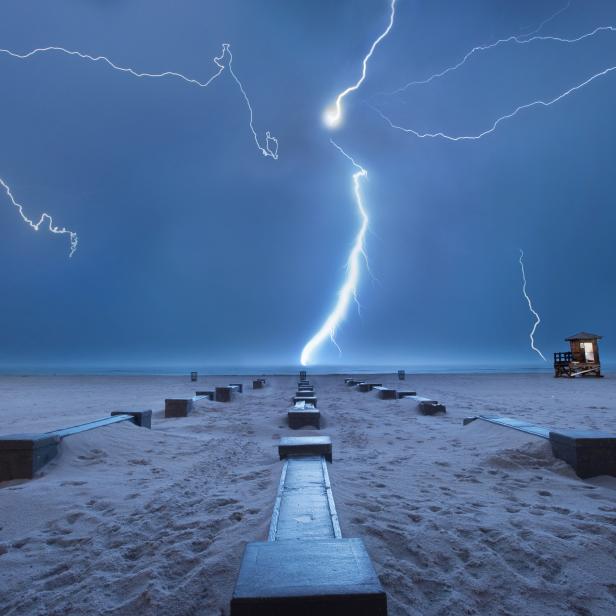
When Lightning Strikes Sand, It Creates Bizarre Glass Sculptures
These pieces of art are Mother Nature's coolest tricks.
When lightning strikes a sandy beach, something amazing happens: it creates glass sculptures. You might've seen this phenomenon depicted in the 2002 Reese Witherspoon romcom Sweet Home Alabama, or maybe in a viral photo that circulated the internet in 2013. What both examples may have lacked in scientific accuracy they certainly made up for by shedding light on one of Mother Nature's coolest tricks.
Mother Nature, Or Sandcastle Matt?
"Sweet Home Alabama" did get something right — when super hot lightning (at least 1,800 degrees Celsius/3,272 degrees Fahrenheit) hits sandy beaches high in silica or quartz, it fuses the sand into silica glass beneath the ground. That means you can actually dig up petrified lightning if you know where to look. The movie portrays these glass sculptures as root-like, but fulgurites, as the glass art is called, actually look more like rocky tubes than glass tree roots. They're typically short and brittle. As for the viral photo? It's not a fulgurite — it's a piece of driftwood covered in drips of wet sand by an artist named Sandcastle Matt. Go figure.
Good Luck, Sand Dwellers
Before you plunge into the sand, know that this is more of an anomaly than something lightning does all the time, and it takes careful excavation to unearth a fulgurite without crumbling it. Still, though it's even more rare, there's a chance that you won't have to dig the tubes up at all. Glass can withstand erosion, so you might happen upon a piece of petrified lightning above ground. Be sure to let us know if you do!
This article first appeared on Curiosity.com.