Science Photo Library - STEVE GSCHMEISSNER
We Finally Know How Tardigrades Survive Deadly Radiation
Bravery isn't quantifiable, but we think it can be pretty accurately measured in just one glance at the Charles Kuonen Suspension Bridge. As of its August 2017 opening, this structure is the longest pedestrian suspension bridge on the planet. It's beautiful, impressive, and vertigo-inducing. Would you cross?
Don't Look Down
You'll find the bridge in Randa, Switzerland, and it looks like something out of a fairy tale. The bridge, opened in August 2017, cuts through the picturesque Swiss Alps at a dizzying height of 282 feet (86 meters) above ground at its highest point. That's the height of 16 giraffes stacked one on top of the other. (Curiosity does not endorse giraffe-stacking.)
The path is so thin (25.5 inches/65 centimeters) and long (1,620 feet/494 meters), it barely looks physically possible. Apparently, it's sound, but we aren't exactly racing to go test that out ...
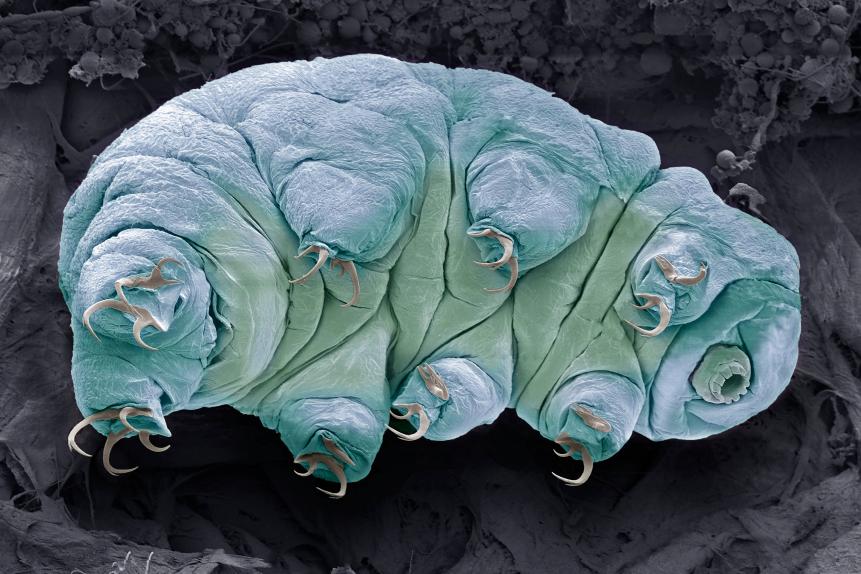
STEVE GSCHMEISSNER/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY
Ten Minutes of Beautiful Terror
Engineers from Swissrope and Lauber cableways built this record-breaking bridge in just 10 short weeks. With its completion, it's now the longest suspension bridge in the world, surpassing the glass-bottomed bridge across the Zhangjiajie Canyon in Hunan province, completed in 2016. One look at the Swiss pathway begs the question: WHY?! Before this walkway was erected, a different path connected the two sides of the valley, but it was damaged by rock falls. The height of the new bridge may seem unnecessary, but it keeps the path out of the rocky danger zone.
Maintaining a bridge here is quite the gift to hikers, who would otherwise have to hike four hours to get to and from the towns of Zermatt and Grächen. With the Charles Kuonen Suspension Bridge, the trek is now 10 minutes — if you've got the guts, anyway. If you don't want to look down while traversing the Swiss Alps valley via this bridge, just look around you. The Matterhorn, Weisshorn, and the Bernese Alps are visible in the distance: a view that might just be worth the acrophobic terror.
This article first appeared on Curiosity.com.