Getty Images
There Are at Least 4 Ways a Black Hole Could Kill You
Do we really stand a chance when it comes to black hole?
Let's face it: Black holes are terrifying. A point in space with so much gravity that not even light can escape? Human beings don't stand a chance. But before you go worrying over what it might feel like to be sucked into the gaping maw of a black hole, we've got news for you: Black holes are so lethal that you could die in a handful of ways before you even reach the event horizon. Below, we've laid out four options for death by black hole, courtesy of theoretical astrophysicist Katie Mack. Sweet dreams!

Gettty Images/MARK GARLICK/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY
Spaghettification
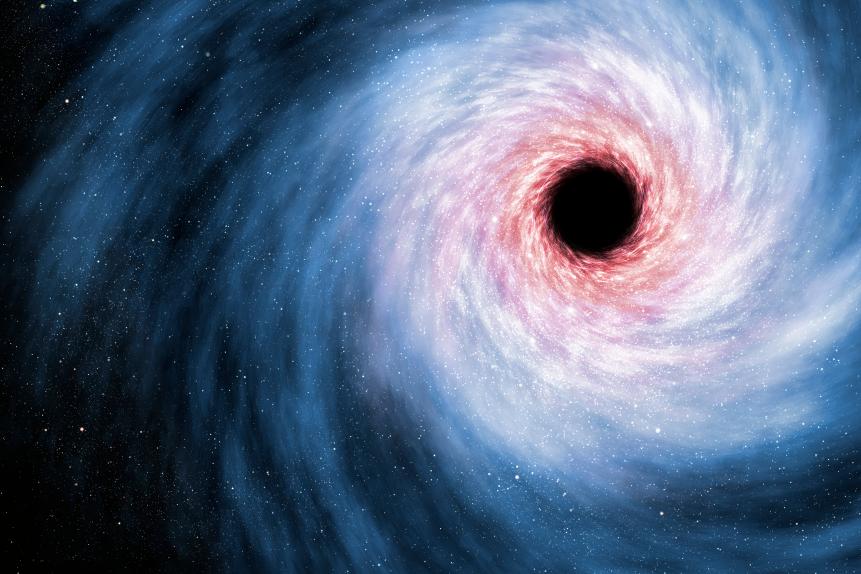
Black holes form when a massive object, like a star, collapses and squeezes all of its mass into an impossibly small point with infinite density, known as a singularity. That much mass in that small of a space leads to a gravitational field so strong that once you've gotten close enough and passed the point of no return (known as the event horizon), you'd have to go faster than the speed of light to escape. That's impossible, so you're stuck there, being stretched by the intense gravity until you're a noodle of your former self.
"Let's say you find the black hole that's the same mass as a star and there's nothing else around it; it's just a black hole by itself," Mack explained to Curiosity. "As you get really close, you get stretched out into spaghetti by the tidal forces. The force on your feet is stronger than the force on your head and it stretches you out, thus spaghettification."
Fried by Accretion Disk
But here's the thing: We've never actually detected a black hole this simple. That makes sense when you think about it: Because they don't let light escape, black holes without anything around them are invisible. But by and large, the black holes we've detected have come to our attention not because of the black hole itself, but because of the glowing, rotating mass of superheated material around it known as an accretion disk. If you encountered a black hole's accretion disk, well, good luck keeping your DNA intact.
"A lot of times we see black holes because there's a black hole and a star orbiting each other and the black hole is pulling stuff off of the star and creating this disk of material that's falling into the black hole," Mack says. "We can see that because as the material is falling in, it heats up and it radiates these super powerful X-ray photons. That would kill you."
Zapped by Plasma Jet
If you happen upon a supermassive black hole at the center of a galaxy (like Sagittarius A*, the black hole at the center of the Milky Way), you've got another hazard to deal with: the gigantic beam of plasma blasting from each end. That accretion disk we mentioned doesn't just produce radiation; the matter within it experiences so much friction that it actually heats up into a magnetized plasma. Combine that powerful magnetic field with the black hole's powerful gravity, and you get a blinding pillar of magnetized plasma that erupts out of each end of the black hole.
"Those jets would also be very dangerous to be around," Mack assures us.
Incinerated by Firewall
This one is more theoretical but just as terrifying: The moment you pass the event horizon, you're incinerated on the spot. This is known as the firewall hypothesis, which was conceived in 2012 by a quartet of researchers as a way to solve a nagging problem with black holes — that is, the fact that they kinda sorta break the laws of physics. Information can't be destroyed, according to a principle called unitarity, but it sure seems like black holes are destroying information.
As a solution to that information problem, in the 1970s, Stephen Hawking and Jacob Bekenstein proposed that the event horizon of a black hole produces what's now known as Hawking radiation: entangled pairs of particles that each shoot one particle of the pair out as radiation and the other into the black hole. All that radiation makes the black hole start to evaporate, at which point that black-hole-doomed particle comes back out: no information destroyed! But that particle still needs to be entangled with a particle that falls in — that is, the exiting particle needs to be entangled with the long-gone radiation particle and with a newly doomed black-hole particle — which is impossible.
The firewall hypothesis fixes this problem by saying that the new entanglement is broken the moment it forms, leading to massive quantities of energy at the event horizon that incinerate anything that tries to pass through. If the plasma beam, accretion disk, and spaghettification don't get you, the firewall (theoretically) will.
This article first appeared on Curiosity.com.