evandrorigon
Food Growers Use AI and Robotics to Tackle Pest Problem
Farmers around the world face serious challenges in growing food more effectively. Climate warming increases the risk of crop damage from insects, fungi, and bacteria. So to manage the threat farms are turning to artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, and computer vision to target pests more effectively.
In 2019 the United Nations reported on the pest burden causing crop losses of between 20 and 40 percent of global production each year. Damage from plant diseases, it said, costs the world economy an estimated $220 billion annually, and invasive insects around $70 billion.
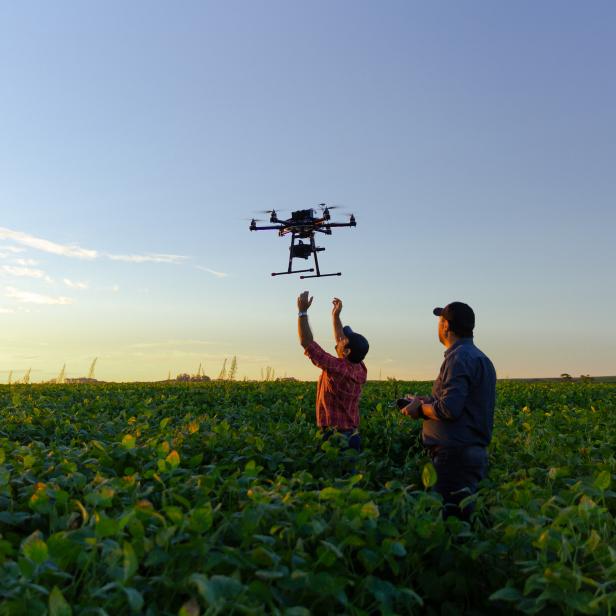
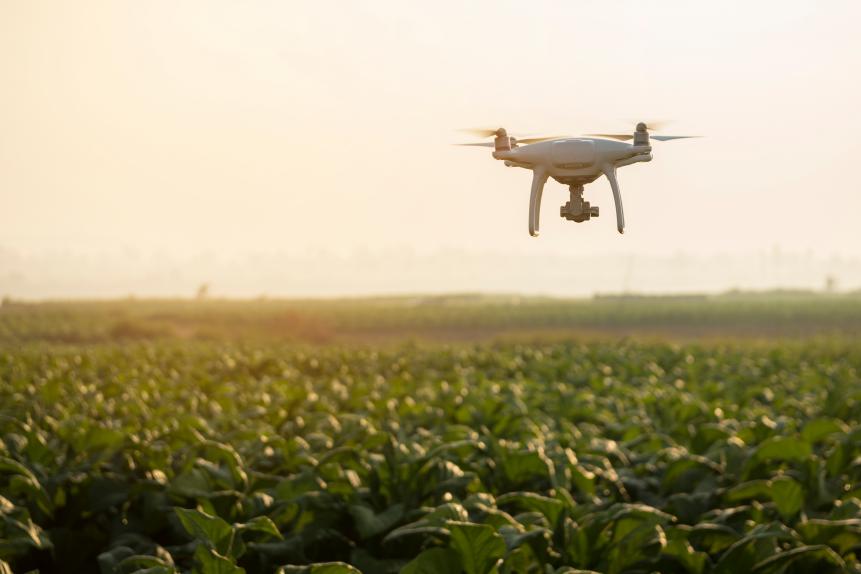
Smart farming is one way to combat the problem, using AI and robotics to zap bugs and reduce reliance on pesticides while addressing skilled worker shortages and adapting to climate change. Technologies include soil and crop sensors, satellite and drone monitoring, plus computer vision and AI data analysis to reduce the number of affected plants and increase crop yields.
Insect monitoring services like the UK’s Spotta offer targeted real-time data on invasive species. The company uses internet-connected dry traps to catch red palm weevils that attack date palms, causing more than $1 billion of losses in the Middle East, Africa, and North America each year.

Mr.kitsadakron Pongha / EyeEm
Traps alert plantation workers to trees infested with weevils so they can eliminate them before they cause any real damage. And this targeted approach means less pesticide is used, reducing the impact on other species.
Similarly the Californian agriculture technology startup FarmSense uses optical sensors and machine learning algorithms trained to find and track insects in real-time. With non-native invasive insect species forecast to increase 36 percent worldwide by 2050, these technologies could give farmers a huge advantage in eco-friendly pest control and food growing.
Precision spot spraying linked to AI is another valuable add-on that aims to minimize pesticide and herbicide use. Spraying entire crops can harm insect pollinators like bees and becomes part of agricultural run-off when it is washed out of soil. But targeting weeds or insects using cameras and directed sprays can vastly reduce chemical use.
In the Czech Republic, scientists at Mendel University in Brno have built a prototype robot that patrols greenhouses and can identify the different stages of insect growth. It then applies just enough insecticide to kill individual pests, working 24 hours a day to keep things under control.
Among Dutch cress growers, the answer to a troublesome moth species is killer drones. Koppert Cress grows its product in chemical-free greenhouses and uses small autonomous drones guided by a camera to kill moths on the wing using their rotor blades. The tiny drone fleet is used alongside traps to keep greenhouses pesticide-free.
Companies like Root AI and 80 Acres Farms are banking on indoor growing and AI-controlled systems as the future of farming. In the case of 80 Acres, its pesticide-free indoor farms are monitored by AI every step of the way. Robots do a lot of the work and computer vision lets them know if crops need more nutrients or if pests are causing damage.
Their efforts are part of what analysts say will be a $2.6 billion AI-farming market by 2025. Reimagining how farming operates will be crucial says the World Bank – reducing its greenhouse gas emissions, soil erosion, and biodiversity loss. And technology will play its part in helping farmers improve their all-around crop management.