Muriel de Seze
Rising Sun: Solar Power for Green Transformation
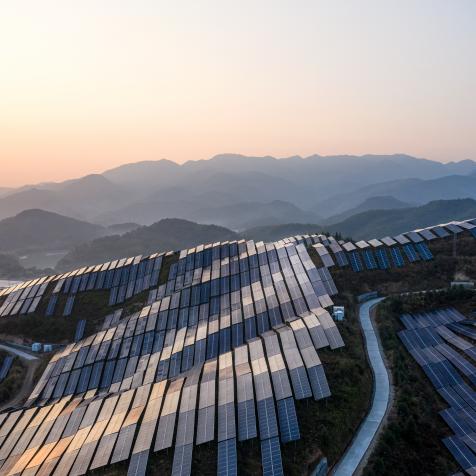
Solar power is due for massive expansion over the next 20 years. Its confirmation by the International Energy Agency as the cheapest, fastest growing renewable energy source will see it leapfrog coal and gas-fired power in most countries.
The coronavirus pandemic saw air quality improvements across the world as factory and transport emissions dropped off. This resulted in a surge of solar output in nations like India, but it is ongoing research and innovation that is driving solar energy forward.
Flexibility Leads to Innovation

typo-graphics
Developments like floating photovoltaic farms (or floatovoltaics) that sit on the surface of lakes or lagoons, can also reduce evaporation and conserve water. Meanwhile, solar cells integrated into buildings and clothing make virtually any surface capable of energy generation.
Low cost, lightweight organic solar cells that use conductive polymers rather than silicon are making these types of breakthrough possible.
Organic solar cells gather larger amounts of light with fewer materials and can be printed like ink onto flexible or transparent films to fit windows or entire walls. Despite this, they are not as stable as silicon-based photovoltaic cells and degrade more quickly. Florida State University is experimenting with the mineral perovskite mixed with different elements to improve efficiency, stability, and overall performance.
Flexible organic solar panels create new ways of gathering and storing energy from the sun. One firm has created flexible film panels that both harvest sunlight and store energy locally to power homes off-grid. Solivus’ panels are one-tenth the weight of traditional panels, contain no rare earth or toxic materials, and last for 20 years. Its plans include covering the roofs of industrial buildings and selling separate ‘arc’ units for home use.
Bifacial solar cells are another worthy innovation. Their dual-surface panels can collect sunlight reflected from the ground, generating more electricity than conventional designs. By 2030, more than half of all photovoltaics sold are likely to be bifacial, including transparent double-sided panels that can operate on farmland used to grow crops at the same time.
Redesigning solar panels could lead to even more improvements. British and Portuguese researchers have discovered that making the panel’s surface more like a checkerboard improves diffraction and the amount of sunlight absorbed by 125 percent. Their breakthrough could lead to thinner, lighter, and more flexible panels that can be used to power homes and industry.
One of the British team, Christian Schuster said: “In principle we could deploy ten times more solar power with the same amount of absorber material: ten times thinner solar cells could enable a rapid expansion of photovoltaics, increase solar electricity production, and greatly reduce our carbon footprint.”
What's It Made Of?

WLADIMIR BULGAR/SCIENCE PHOTO LIBRARY
Special materials used to gather indirect or diffuse ambient light can also now be incorporated into textiles. These luminescent solar concentrators are applied in gels to clothing fabrics and can be used to power mobile devices. For a world so used to static charging, the promise of portable solar energy unlocks another level of personalized energy.
But an even more revolutionary development could make solar energy a 24-hour power in warmer regions. Thermoradiative cells generate electricity by radiating infrared light (as heat) into the surrounding atmosphere. So panels covered in thermoradiative cells and pointed at the cool night sky would create energy by losing heat.
Thermoradiative panels could also be made to work during the day–by shielding from direct sunlight or turning them away from the sun – producing electricity round the clock and making solar power the ‘go to’ source for dependable energy.