It Wasn't Rose's Fault! All the Doors that Contributed to Jack's Death!
So, was there room for Jack on that piece of wooden debris? What's up with the debate about the door in the basement?
More than 100 years since the tragic event and two decades after the initial release of Titanic, there have been multiple "door" conspiracy theories. Let's break down two of those popular theories.
Rose's Door
Despite director James Cameron, leading actress Kate Winslet, and leading actor Leonardo DiCaprio’s repeated efforts to settle the most iconic movie controversy of all time, audiences are still obsessed with the debate over whether or not Jack and Rose could have both fit onto the wooden debris and survived. So, was there room for Jack?

CBS Photo Archive
In a 2012 Mythbusters episode, Jamie Hyneman and Adam Savage did an experiment using an exact replica of the wooden piece from the movie, and the two proved that if they had tied Rose’s life jacket to the bottom of the door to reinforce its buoyancy, they would’ve managed to stay afloat.
However, their conclusion was debunked when director Cameron claimed that the freezing water and Jack’s hyperthermia would have made the life jacket solution impossible. He also said that the debate is beyond the point the movie was trying to make, which is focused on the tragic love story of Jack and Rose, not physics.
The largest fragment of debris recovered from the real Titanic, now displayed in the Maritime Museum of the Atlantic in Halifax, Nova Scotia, is a piece intricately carved “wreckwood” that is believed to be a panel above the doorframe of the first-class lounge. The museum’s website states that a replica of a large piece of carved oak paneling was built for the film based on the artifact from the museum’s Titanic collection, which was known as the “door” used in the climactic death scene where Rose clings to the floating wreckage. Unfortunately, the size of the oak debris coupled with the weight of a hypothermic Rose on top could work, but not if Jack’s additional weight was added to it.
Cinematic choice or not, science has proven the movie’s ending to be reasonable. Now we know that Jack didn’t die for nothing and did indeed sacrifice himself to save the love of his life!
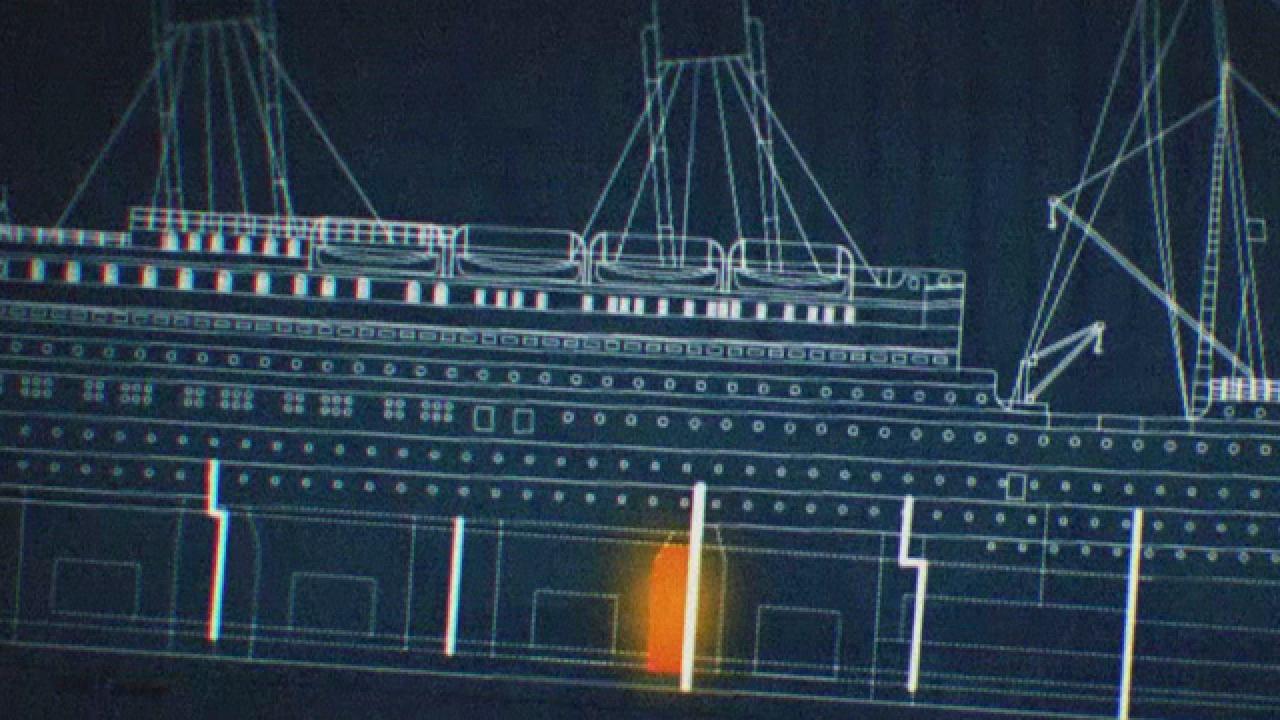

The Basement Door
Although the Science Channel special doesn't cover Rose's door, it does go into theories about the door in the basement and a fire in the bunker. Did this fire weaken the bunker? Was the door in the basement poorly constructed so it didn't stand a chance once water started flowing in?
For more discussion on the Titanic's demise, tune in to TITANIC: CONSPIRACY OF FAILURE on Sunday, 3/15 at 8:30pm ET or watch it on SCI GO.